“It was an incredible realisation seeing the results emerge and remain consistent throughout the extensive independent analyses and robustness tests,” said co-author Måns Holmberg, a researcher at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, USA.
DMS and DMDS are molecules from the same chemical family, and both are predicted to be biosignatures. Both molecules have overlapping spectral features in the observed wavelength range, although further observations will help differentiate between the two molecules.
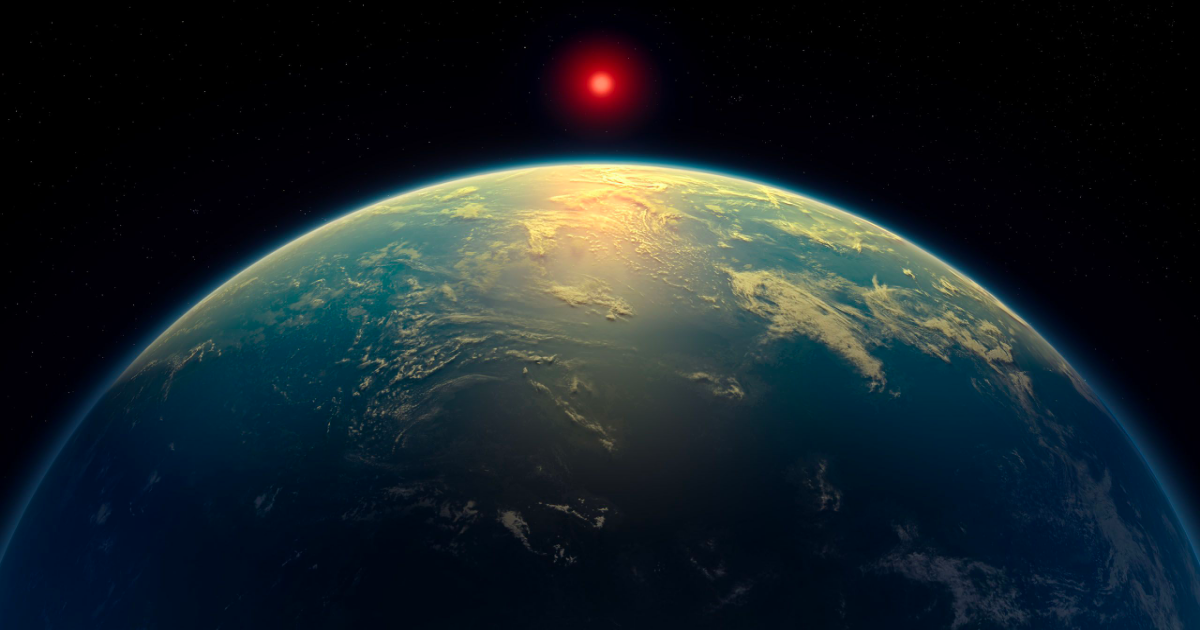
However, the concentrations of DMS and DMDS in K2-18b’s atmosphere are very different than on Earth, where they are generally below one part per billion by volume. On K2-18b, they are estimated to be thousands of times stronger – over ten parts per million.
“Earlier theoretical work had predicted that high levels of sulfur-based gases like DMS and DMDS are possible on Hycean worlds,” said Madhusudhan. “And now we’ve observed it, in line with what was predicted. Given everything we know about this planet, a Hycean world with an ocean that is teeming with life is the scenario that best fits the data we have.”
Madhusudhan says that while the results are exciting, it’s vital to obtain more data before claiming that life has been found on another world. He says that while he is cautiously optimistic, there could be previously unknown chemical processes at work on K2-18b that may account for the observations. Working with colleagues, he is hoping to conduct further theoretical and experimental work to determine whether DMS and DMDS can be produced non-biologically at the level currently inferred.
“The inference of these biosignature molecules poses profound questions concerning the processes that might be producing them” said co-author Subhajit Sarkar of Cardiff University.
“Our work is the starting point for all the investigations that are now needed to confirm and understand the implications of these exciting findings,” said co-author Savvas Constantinou, also from Cambridge’s Institute of Astronomy.
“It’s important that we’re deeply sceptical of our own results, because it’s only by testing and testing again that we will be able to reach the point where we’re confident in them,” Madhusudhan said. “That’s how science has to work.”
While he is not yet claiming a definitive discovery, Madhusudhan says that with powerful tools like JWST and future planned telescopes, humanity is taking new steps toward answering that most essential of questions: are we alone?
“Decades from now, we may look back at this point in time and recognise it was when the living universe came within reach,” said Madhusudhan. “This could be the tipping point, where suddenly the fundamental question of whether we’re alone in the universe is one we’re capable of answering.”
The James Webb Space Telescope is a collaboration between NASA, ESA and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The research is supported by a UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) Frontier Research Grant.
To learn more about Hycean worlds, visit hycean.group.cam.ac.uk.
Reference:
Nikku Madhusudhan et al. ‘New Constraints on DMS and DMDS in the Atmosphere of K2-18b from JWST MIRI.’ The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2025). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/adc1c8